show active network connections and processes | Windows
For a quick overview of which programs or services have an active network connection, they can be listed via simple commands or monitored and analyzed via specific tools.
PowerShell: Get-NetTCPConnection
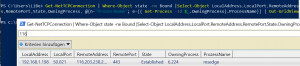
As an alternative to the CMD command "netstat", the command "Get-NetTCPConnection" can be used in PowerShell to display the network connections. The following command line combines Get-NetTCPConnection with Get-Process and Out-GridView. The result is a list of all incoming and outgoing network connections and their processes.
The following line can be easily pasted (Ctrl+C) into Windows PowerShell via the clipboard (Ctrl+V):
Get-NetTCPConnection | Where-Object state -ne Bound | Select-Object LocalAddress,LocalPort,RemoteAddress,RemotePort,State,OwningProcess, @{n="ProzessName"; e={( Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).ProcessName}} | Out-GridViewThanks to Out-GridView, the displayed network connections can be easily sorted and filtered:

(Here connection from Microsoft Edge to a web page with port 443)
Legend:
| LocalAddress | local network address (own address) own IP address or 0.0.0.0 (::) for any address |
|---|---|
| LocalPort | local network port |
| RemoteAddress | Remote device network address |
| RemotePort | Network port of the remote device |
| OwningProcess | Process ID (PID) of the service which establishes or receives the connection. |
| ProzessName | ProcessName of "Get process" |
State
| Listen | wait for connection Mostly on any own address (0.0.0.0) and a local port. A connection can be established from a remote device to the local port listed here. |
|---|---|
| Bound | Socket created (bind), but no further call (listen, accept, connect, close) |
| Established |
Connection established
|
| SynSent |
outgoing connection attempt |
| SynReceived |
incoming connection attempt |
| Closing | Both sockets finished, but not all data sent yet |
| CloseWait | The remote device has terminated the connection |
| Closed | Socket is not used |
| TimeWait | Socket waits after closing to still process packets on the network |
| LastAck | The remote device has terminated the connection, the socket is closed, wait for confirmation |
| FinWait1 | Socket is closed and the connection is terminated |
| FinWait2 | Connection terminated, socket waits for remote device to terminate |
How does the command line compose itself, in order
Get-NetTCPConnection shows all active network connections of the PC:
PS C:\Users\LiBe> Get-NetTCPConnection
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State AppliedSetting
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- --------------
:: 445 :: 0 Listen
:: 135 :: 0 Listen
...
192.168.1.198 49808 116.203.238.206 443 Established Internet
....As usual in PowerShell, a pipe and "where" can be used to filter specifically:
PS C:\Users\LiBe> Get-NetTCPConnection | where RemoteAddress -Like "116*"
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State AppliedSetting
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- --------------
192.168.1.198 49827 116.203.238.206 443 Established InternetIn the standard output the process ID is missing, this can be displayed as follows:
PS C:\Users\LiBe> Get-NetTCPConnection | where RemoteAddress -Like "116*" | Select-Object LocalAddress,LocalPort,RemoteAddress,RemotePort,State,OwningProcess | Format-Table
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State OwningProcess
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- -------------
192.168.1.198 49843 116.203.238.206 443 Established 6224The Get-Process command can be used to read the ProcessName for the PID.
PS C:\Users\LiBe> Get-Process -Id 6224
Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) CPU(s) Id SI ProcessName
------- ------ ----- ----- ------ -- -- -----------
288 19 10924 24952 1,89 6224 1 msedgecombined:
PS C:\Users\LiBe> Get-NetTCPConnection | Select-Object LocalAddress,LocalPort,RemoteAddress,RemotePort,State,OwningProcess, @{n="ProzessName"; e={( Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).ProcessName}} | Format-Table
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State OwningProcess ProzessName
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- ------------- -----------
:: 49670 :: 0 Listen 708 services
:: 49669 :: 0 Listen 2760 spoolsv
:: 49668 :: 0 Listen 2096 svchost
...
:: 49665 :: 0 Listen 600 wininit
:: 49664 :: 0 Listen 744 lsass
:: 445 :: 0 Listen 4 System
:: 135 :: 0 Listen 992 svchost
0.0.0.0 49849 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 6224 msedge
0.0.0.0 49848 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 7744 msedgewebview2
0.0.0.0 49847 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 7744 msedgewebview2
0.0.0.0 49846 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 7744 msedgewebview2
....
0.0.0.0 49713 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 8700 SystemSettings
0.0.0.0 49707 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 6224 msedge
0.0.0.0 49673 0.0.0.0 0 Bound 2716 svchost
192.168.1.198 49849 116.203.238.206 443 Established 6224 msedge
192.168.1.198 49820 40.97.120.130 443 Established 5252 SearchHost
192.168.1.198 49707 192.168.1.166 8009 Established 6224 msedge
192.168.1.198 49673 20.199.120.85 443 Established 2716 svchost
...netstat: Windows / Linux
The netstat command is available in both Linux and Windows and provides the ability to view all network connections and open ports. It is called in Windows from the command prompt, by entering the following command:
netstat -ano The parameters -ano mean:
- a means: all connections
- n: Addresses and port numbers numeric
- o: additionally display the PID (i.e. which process is behind it)

the status
LISTENING means: The client listens for this port. It therefore waits until another network device establishes a connection to it.
SYN_SENT: The client is establishing a connection and waiting for the response.

ESTABLISHED according to: Connection established.
Filter
If the output should contain too many entries, the output can be filtered by the command "find", i.e.

Processes
With the parameter /b netstat tries to display the underlying process based on the PID, for this administrator rights are required:

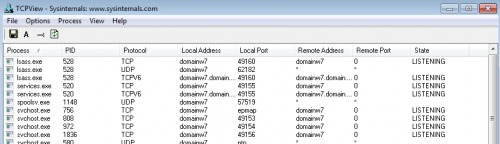
TCPView
With the free tool TCPView, similar to Get-NetTCPConnection, all connections can be displayed. The tool consists of a simple .exe file and does not need to be installed.
technet.microsoft.com/de-at/sysinternals/bb897437.aspx
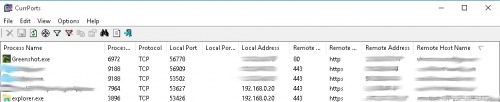
CurrPorts
The tool CurrPorts from nirsoft, which is also free of charge, offers an extended range of functions. The additional functions include notification of new connections, filters and the option to record a log file. CurrPorts also consists of a simple exe file and, like TCPView, does not need to be installed.
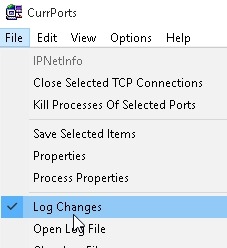
Certain services can be excluded by right-clicking and "Exclude in Filter", or only certain services can be observed with "Include in Filter".
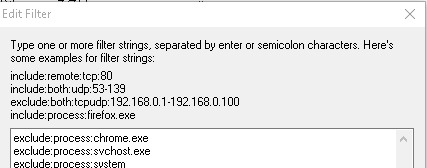
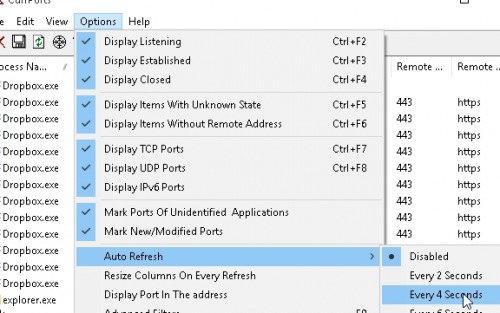
An autorefresh interval can be set so that the view is refreshed automatically:
Tooltip notification via "Tray Balloon On New Ports

Browser - Inspect
To view the communication of the browser when calling a web page, all modern browsers include the ability to make network calls visible. In Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Firefox and Microsoft Edge with a "right click" on the web page and: "Examine element".

in the Network tab the loaded elements are displayed:

Wireshark
Wireshark is an extremely powerful tool. The open source program offers experienced users the possibility to analyze network traffic in detail. However, Wireshark is not only suitable for specialists. Thanks to the numerous filters and functions, anyone should be able to get an overview of the network traffic very quickly:
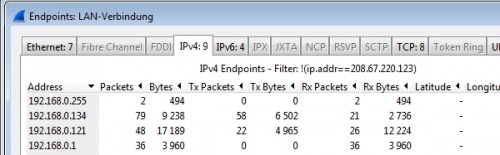
For example, under Statistics / Endpoints, all devices to and from which a network connection has been initiated can be displayed:
Windows Performance Toolkit
A trace from the operating system's point of view can be created using the Windows Performance Toolkit. In addition to the processes and events, their network communication is also logged, as an example for a logon trace
Conclusion
For a quick overview of active network connections, a simple command in PowerShell: Get-NetTCPConnection or the netstat command prompt is sufficient. For a better overview or more details, special programs can be used, up to the network sniffer: Wireshark, which can record the complete network traffic.
 ({{pro_count}})
({{pro_count}})
{{percentage}} % positive
 ({{con_count}})
({{con_count}})