WiFi and LAN network cable simultaneously - Internet access
What actually happens when WiFi and the network cable are connected at the same time? The routing table provides the answer to this question. By adjusting the routing or the metric in the TCP/IP settings of the adapters, the desired behavior can be set. If you want to see the settings noted here in action, you can do so in a short video.
Aim of this article
Configuring Internet accesswith more than one network adapter
e.g. WiFi and LAN
Effort
Reading time: approx. 7 MinutesPrerequisite
a little network basic knowledgeand a Windows computer
Change access: Metric
Each network adapter has a "metric" in its TCP/IP settings. In case of equal entries in the routing table, as an example two adapters with a possible internet connection, the adapter with the lower metric is used for access to the internet. To influence which adapter is used for access, the metric for each adapter can be set to a specific value in the network connection settings of "Automatic metric".
Searching for "View network connections" 
"Control Panel > Network and Sharing Centre"
The setting is done by right-clicking on the respective adapter: "Properties", "Internet Protocol, Version 4 (TCP /IPv4)", "Advanced", "IP Settings":
For example, if the Ethernet adapter (network cable) is set to a fixed value of 30 and the WiFi adapter is set to 10, the call to the Internet would take place via the WiFi adapter and the access to the subnet of the Ethernet adapter via its cable.
In Detail
In the following example, the computer uses a wired network card (Ethernet) with the IP address: 192.168.0.10 and a WiFi card with the IP address 192.168.1.169.
Information about the IP addresses and the network adapters can be read out with the command ipconfig /all.
To start, I just connect the Ethernet network cable:
Ethernet only
The routing table can be displayed using the "route print" command at the command prompt.
My LAN connection shows the following routing entries:
C:\Users\LiBe>route print
IPv4 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.10 20
127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
192.168.0.10 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
192.168.0.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.1.10 281
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
===========================================================================
Persistent Routes:
NoneThe first line is interesting:
0.0.0.0 means all destinations not explicitly in the routing table are forwarded to the gateway.
More precisely it means:
The network adapter with IP: 192.168.0.10 forwards requests for addresses that do not match any range in the table to the gateway: 192.168.0.1. So the gateway is used if the called address is in an unknown network range. The gateway, here with the address 192.168.0.1, is the address of the router; an address in an unknown network area is an address that is not located in a specified local LAN, in this case on the Internet.
WiFi only
When I unplug the network cable and connect to the WiFi, the routing table looks like this:
So again "route print" in the command prompt:
C:\Users\LiBe>route print
IPv4 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.169 25
127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
192.168.1.169 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
192.168.1.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
===========================================================================
Persistent Routes:
NoneMy WiFi router has the IP: 192.168.1.2, the WiFi adapter has the address 192.168.1.169. Again, all requests that are in a network that is not listed are routed to the Internet via the entry 0.0.0.0. It will be exciting if I now additionally reconnect the network cable:
Ethernet and WiFi
C:\Users\LiBe>route print
IPv4 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.169 25
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.10 20
127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
192.168.0.10 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
192.168.0.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
192.168.1.169 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
192.168.1.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.0.169 281
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.0.10 281
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.169 281
===========================================================================
Persistent Routes:
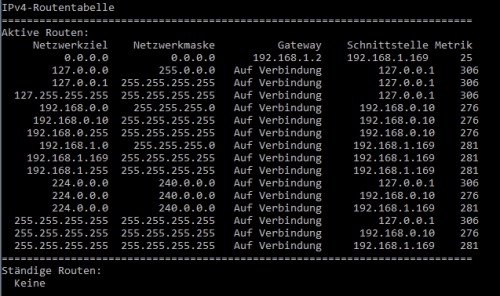
NoneNow it becomes problematic: In the table there are two identical entries (0.0.0.0) for the connection to the Internet.
In this case the computer tries to use the entry with the smaller metric first, so in our case the Ethernet cable (adapter with the address: 192.168.0.10).
For devices in the 192.168.1.x network, according to the entry:
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 On-Link 192.168.1.169 the network adapter with the IP: 192.168.1.169 is used, i.e. our WiFi adapter.
For devices in the network 192.168.0.x is used according to the entry:
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 On-Link 192.168.0.10 the network adapter with the IP: 192.168.0.10 is used.
Customize metrics
If I use a higher metric for the network adapter than for the WiFi adapter, WiFi is used by default.
The setting is transferred to the routing table:

The metric could also be set from the command prompt:
route change 0.0.0.0 MASK 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 metric 1
with route change 0.0.0.0 MASK 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 metric 1 -p the setting remains even after a connect and disconnect, or after a reboot.
If the IP address is assigned by a DHCP server, this can specify the metric:
Option "Default Router Metric Base", see https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc977349.aspx;
The default values are described on this page: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/299540/an-explanation-of-the-automatic-metric-feature-for-ipv4-routes
Advanced: Customize routing table
In order to edit the routing table, we need to start it as administrator:

with the command: route delete 0.0.0 mask 0.0.0 192.168.0.1 we can specifically delete the connection to the Internet for the Ethernet connection (network cable).
C:\Windows\system32>route delete 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1
OK!
C:\Windows\system32>The computer is still connected to the local LAN,
Requests to the Internet go via the WiFi adapter: 192.168.1.169
Requests to the local LAN of the Ethernet adapter via the network cable: 192.168.0.10
Additional routes can be entered with the "route add" command. The changes to the routing table are lost again after the PC is restarted. For permanent changes the parameter "-p" can be used.
Video
I recreated the behavior of changing the metric in the following video:
 ({{pro_count}})
({{pro_count}})
{{percentage}} % positive
 ({{con_count}})
({{con_count}})

